Carbohydrates are essential macronutrients that serve as the primary source of energy for the body. They are found in a wide variety of foods and can be classified into two main types: simple carbs and complex carbs. Understanding the differences between these two types of carbohydrates is crucial for making informed dietary choices that support overall health and well-being. This article delves into the distinctions between simple carbs and complex carbs, their impact on the body, and how to incorporate them into a balanced diet effectively.
Simple Carbs vs. Complex Carbs
What are Simple Carbs?
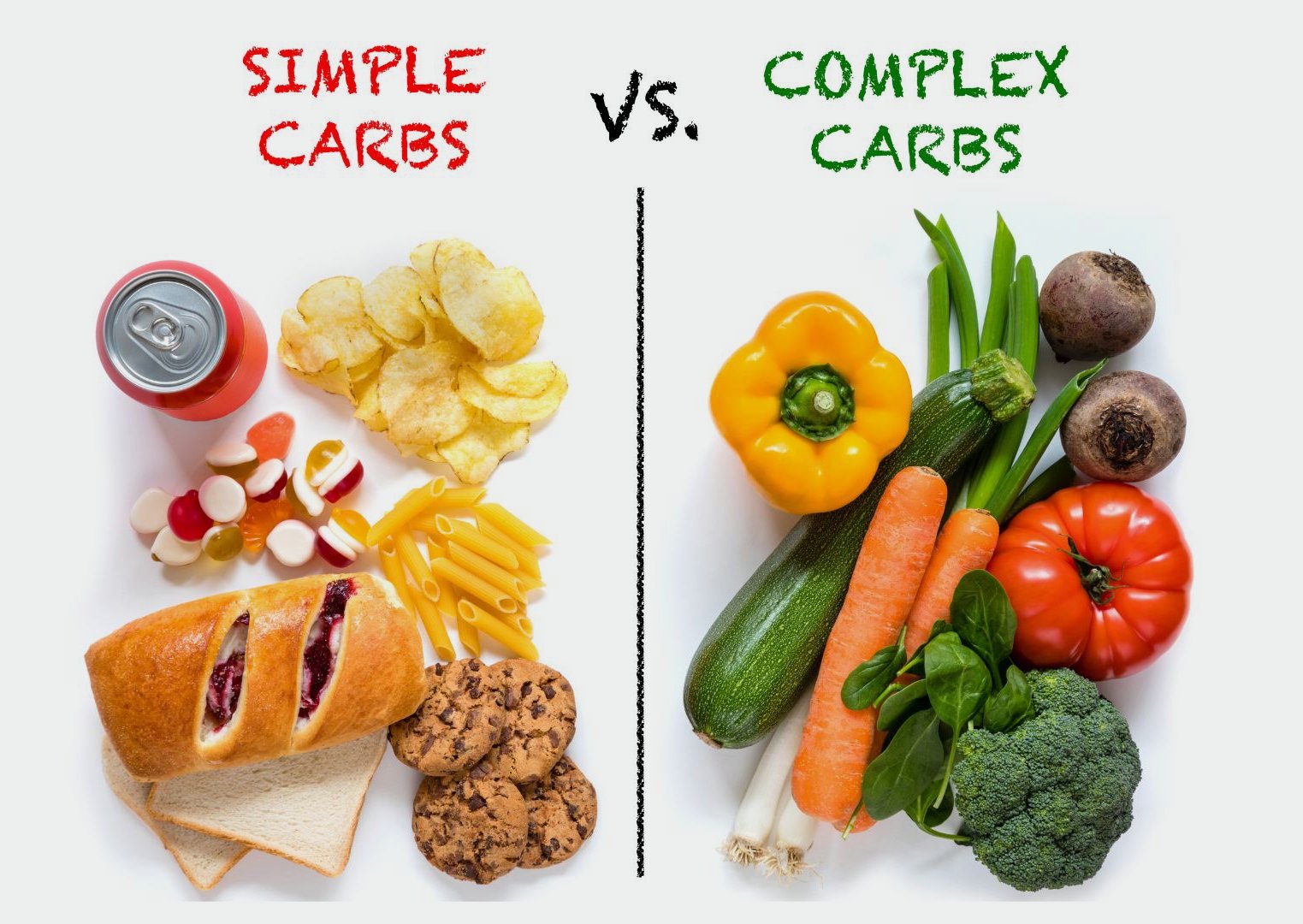
Simple carbohydrates, also known as simple sugars, are composed of one or two sugar units (monosaccharides or disaccharides). These sugars are quickly digested and absorbed by the body, leading to a rapid increase in blood sugar levels. Common sources of simple carbs include:
- Fruits: Such as bananas, grapes, and mangoes.
- Vegetables: Particularly starchy ones like corn and potatoes.
- Dairy products: Milk and yogurt, which contain lactose.
- Refined sugars: Found in processed foods like candy, soda, and pastries.
Simple carbs provide a quick burst of energy, but can lead to spikes and crashes in blood sugar levels if consumed in excess.
What are Complex Carbs?
Complex carbohydrates are made up of longer chains of sugar molecules, which take longer for the body to break down and digest. This slow digestion results in a more gradual and sustained release of glucose into the bloodstream, providing a steady source of energy. Common sources of complex carbs include:
- Whole grains: Include oatmeal, brown rice, quinoa, and whole wheat.
- Legumes: Beans, lentils, and chickpeas.
- Vegetables: Leafy greens, broccoli, carrots, and peppers.
- Fruits: Apples, berries, and citrus fruits, which also contain fiber.
Complex carbs are rich in fiber, vitamins, and minerals, contributing to improved digestive health, prolonged satiety, and stable energy levels throughout the day.
Key Differences Between Simple and Complex Carbs
Simple Carbohydrates vs. Complex Carbohydrates
| Feature | Simple Carbohydrates | Complex Carbohydrates |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | 1–2 sugar units (monosaccharides/disaccharides) | Long chains of sugar molecules (polysaccharides) |
| Digestion Speed | Fast – quickly absorbed | Slow – gradual digestion |
| Impact on Blood Sugar | Rapid spike in blood sugar | Steady release of glucose |
| Nutrient Content | Low – often lacks fiber and nutrients | High – rich in fiber, vitamins, and minerals |
| Sources | Candy, soda, white bread, sugary cereals | Whole grains, legumes, vegetables, fruits |
| Effect on Satiety | Short-term energy, quick hunger return | Longer satiety, sustained energy |
| Health Impact | Can lead to weight gain, insulin spikes | Supports digestion, energy, and weight management |
1. Digestion and Absorption:
- Simple carbs are quickly digested and absorbed, leading to rapid spikes in blood sugar levels.
- Complex carbs take longer to digest, resulting in a slower and more sustained release of glucose into the bloodstream.
2. Nutritional Value:
- Complex carbs are typically higher in fiber, vitamins (like B vitamins and vitamin E), and minerals (such as magnesium and potassium) compared to simple carbs.
- Simple carbs often lack significant nutritional value beyond providing quick energy.
3. Impact on Health:
- Consuming too many simple carbs can contribute to weight gain, insulin resistance, and an increased risk of type 2 diabetes.
- Complex carbs support overall health by promoting digestive health, maintaining energy levels, and supporting weight management.
Incorporating Carbs into a Balanced Diet
To maintain a balanced diet that includes both types of carbohydrates, consider the following tips:
- Balance and Moderation: Aim to consume a variety of foods rich in complex carbs like whole grains, legumes, and vegetables, while limiting simple carbs from sugary snacks and refined grains.
- Prioritize Whole Foods: Choose whole, minimally processed foods that provide essential nutrients and fiber over refined and sugary options.
- Meal Planning: Plan meals that incorporate a balance of complex carbs, lean proteins, healthy fats, and vegetables to support overall nutrition and satiety.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between simple carbs vs. complex carbs empowers you to make healthier choices that support your energy levels, weight management goals, and overall well-being. While simple carbs provide quick energy, they should be consumed in moderation, ideally as part of a balanced meal that includes proteins and healthy fats. On the other hand, complex carbs, rich in fiber and nutrients, should form the foundation of your diet. By prioritizing whole, nutrient-dense foods like whole grains, legumes, fruits, and vegetables, and being mindful of portion sizes, you can effectively manage your carbohydrate intake. This balanced approach not only stabilizes blood sugar levels, but also promotes satiety and supports digestive health. Incorporating both simple and complex carbs in appropriate quantities ensures a sustainable eating pattern that fosters long-term health and vitality.